From the Journal: Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy
WASHINGTON, October 12, 2021 — The development of wind energy, a renewable, emissions-free energy source, is widely acknowledged as an imperative to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and the impacts of climate change. In recent years, much progress in this realm has been made as the cost of developing wind energy has declined significantly with emerging technologies and incentive policies.
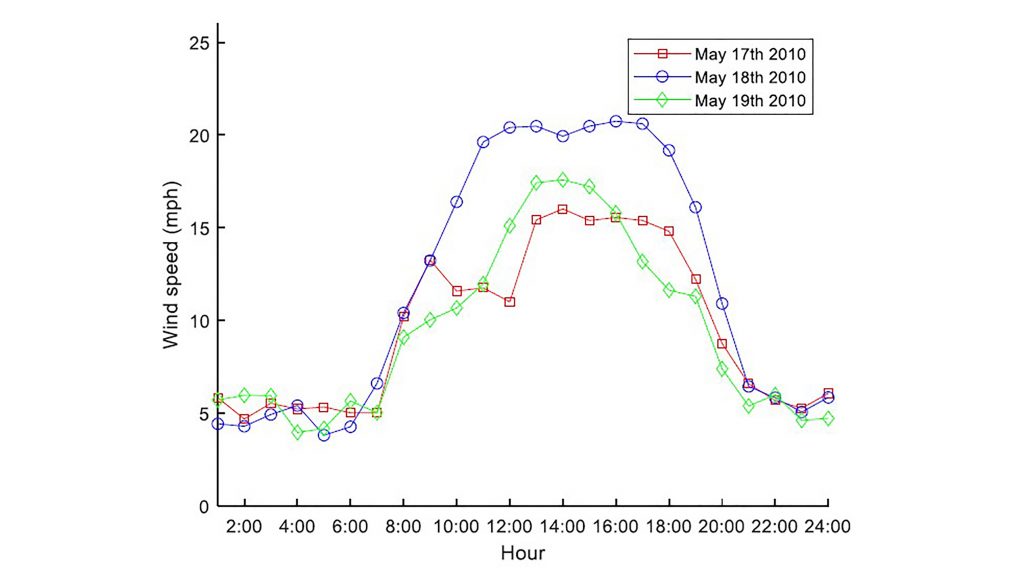
Nevertheless, wind farms, generally located in areas with robust wind resources and typically consisting of multiple turbines that convert wind into clean electricity, can be made more efficient. In Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers from China and the United States examine diurnal and seasonal patterns of wind speeds and their impact on the adequacy of energy production.
“In wind farm planning, decision-makers need to select an appropriate site for wind farm installation,” said co-author Shuwei Miao, from Three Gorges University in Yichang, China. “We developed a seasonal adequacy assessment procedure using historical wind speed data, wind turbine parameters, system peak load, and other important factors that can help inform decisions on wind farm siting and operation.”
Using a two-phase simulation model to simulate diurnal and seasonal wind speed variations, the researchers justify the accuracy of their results by comparing them to actual data collected from a wind site in North Dakota. The results helped them develop the seasonal adequacy assessment procedure.
“Wind speed associates with uncertainty along with the season, terrain, and climate,” said Miao. “And it also determines the energy production potential.
“If a power system contains considerable wind farm capacities, then the capability of system generation to meet system load will be heavily influenced by uncertain wind speed. This capability refers to system adequacy, and the quantitative assessment of system adequacy can be helpful to optimal wind farm planning.”
The first phase of the simulation model examines wind speed probability distribution during 24-hour durations. The second phase considers wind patterns on a seasonal basis. Together, they offer significant insight into the peculiar nuances of the naturally occurring energy resource and how to more efficiently capitalize on them.
“We believe our findings are valuable to wind energy development and production,” said Miao. “When historical wind speed data, wind turbine parameters, and other data for a candidate site in other regions are available, the model and procedure presented in this study can be readily applicable to simulate the wind profile and assess the seasonal system adequacy indices.”
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
Authors
Shuwei Miao, Haoran Xiong, Dan Li, and Yingzhong Gu
Author Affiliations
China Three Gorges University, Global Energy Interconnection Research Institute North America
