New, Enhanced Security of Data Storage and Transmission via Optical "Marked Ghost Imaging" Technology Developed at the National University of Singapore
From the Journal: Applied Physics Letters
WASHINGTON D.C., June 24, 2014 – “Ghost imaging” sounds like the spooky stuff of frivolous fiction, but it’s an established technique for reconstructing hi-res images of objects partly obscured by clouds or smoke. Now a group of researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) is applying ghost imaging to secure stored or shared electronic data.
Described in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, the work establishes “marked ghost imaging” technology as a new type of multi-layer verification protocol for data storage or transmission.
By “ghosting up” data, the scientists can hide the contents of electronic communications from hackers, deconstructing it into multiple foggy files that make no sense on their own and can only be reconstructed by someone who has the right decoder key (technically called a “reference intensity sequence”).
“The sender can send out a huge number of different reference intensity sequences — only one is authentic, and others are counterfeit — for confusing the attackers,” said Wen Chen, an author who conducted the work with NUS professor Xudong Chen.
“This novel method based on ghost imaging can dramatically enhance system security, and it may be straightforward to apply it to other optical security systems,” Chen added.
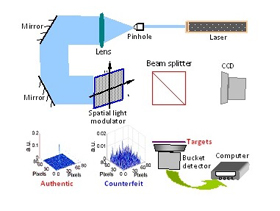 How the Technology Works
How the Technology Works
Information security has become one of the most important social and academic topics in recent years as massive increases in data storage have coincided with rapidly developing modern technologies for accessing that data virtually anywhere. Imaging technology has attracted more and more attention in computer security circles because of its promise to enhance the security of data storage or transmission, which is what led Chen and colleagues to develop their marked ghost imaging technology based on traditional optical ghost imaging.
Traditional ghost imaging uses digital cameras to detect light bouncing directly off of an object as well as light that does not directly bounce from the object to the detector. It allows solid images of objects to be reconstructed by shining light into a beamsplitter and separating it into two correlated beams — one directed at the object and the other, reference arm directed at the camera lens. When these two beams are correlated, they create a silhouette image of the object.
Chen and his colleague report that although virtual computation, using software, is applied, they can do the same thing with real experiments in the future study. Their technology allows them to create highly-sparse reference intensity patterns that act as security keys and lowly-sparse intensity patterns as useful parameters for recovering the target, the information being decoded. To compress the data and confuse the attackers, the reference-arm patterns are then processed to ‘rebuild’ one new reference intensity sequence. This is crucial because requiring only one rebuilt intensity sequence doesn’t increase the system’s complexity, while allowing multiple marks to be hidden.
Future research includes analysis of the upper limit of keys that can be embedded without increasing the system’s complexity and developing greater robustness of the system against attacks.
###
Article Title
Authors
Wen Chen and Xudong Chen
Author Affiliations
National University of Singapore (NUS)
