Futuristic material molybdenum disulfide may find new application for thin-film transistors in extremely high-temperature electronics and sensors
From the Journal: Journal of Applied Physics
Washington, D.C., February 10, 2015 — Many industries are calling for electronics that can operate reliably in a harsh environment, including extreme temperatures above 200° Celsius. Examples of the high temperature applications include turbine engine control in aerospace and electronics or sensors used for drilling operation in oil and gas industry. Although traditional cooling systems can help electronics function at high temperatures, in some applications, cooling may not be possible—or it may be more appealing for the electronics to operate hot to improve system reliability or reduce cost. However, the availability of transistors and circuits for high temperature operation is very limited.
Now a team of researchers from the University of California, Riverside and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute discovered that molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a semiconductor material, may be a promising candidate to make thin-film transistors for extreme temperature applications. In a paper published this week in the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, the researchers report the fabrication of molybdenum disulfide thin-film transistors and their functional performance at high temperatures, demonstrating the material’s potential for extreme-temperature electronics.
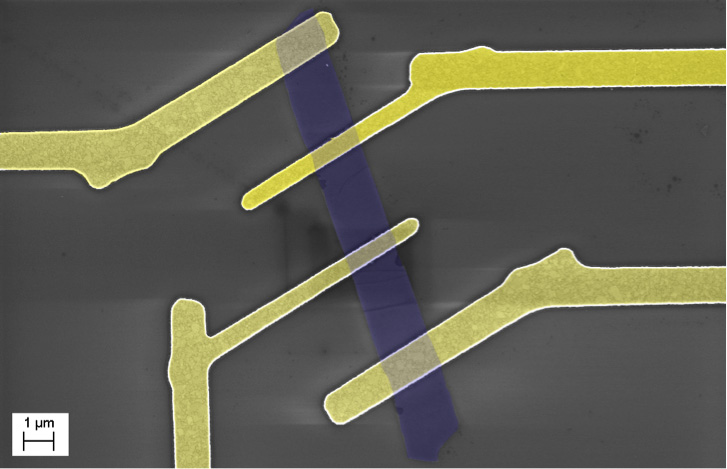
“Our study shows that molybdenum disulfide thin-film transistors remain functional to high temperatures of at least 500 Kelvin [220 Celsius],” said Alexander Balandin, the team leader and a professor at the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the UC-Riverside. “The transistors also demonstrate stable operation after two months of aging, which suggests new applications for molybdenum disulfide thin-film transistors in extreme-temperature electronics and sensors.”
Molybdenite, a mineral of molybdenum disulfide, is an abundant, naturally occurring material, which is commonly used as an additive in lubricants. Molybdenum disulfide synthesized by chemical vapor deposition has been found to be a promising material for manufacturing flexible, thin-film transistors — devices that control the movement of electrons and electric current, like a water faucet.
According to Balandin, molybdenum disulfide belongs to a family called van der Waals materials, which have characteristic layered crystal structure with atomic layers weakly bonded to each other (a type of bonding referred to technically as “van der Waals interactions,” from whence the name derives). The weak connection between atomic sheets enables exfoliation of such materials layer by layer, similar to the process used for obtaining graphene by peeling thin sheets off chunks of graphite. The layered structure also suggests that extremely thin and high-quality layers can also be produced by chemical vapor deposition on industrial scale.
“Although devices made of conventional large-band-gap-semiconductors, such as silicon carbide or gallium nitride, hold promise for extended high-temperature operation, they are still not cost-effective for high volume applications,” Balandin said. “A single-layer molybdenum disulfide shows a band gap of 1.9 eV, which is larger than that of silicon and gallium arsenide. This is beneficial for the proposed application.” The presence of a larger band gap means that a device can be easily switched on and off, a crucial property for transistor’s operation.
A “Hot” New Material
Molybdenum disulfide has recently attracted a lot of interest for device applications, but Balandin’s team is the first to investigate the material’s potential for high-temperature electronics.
Using standard lithography techniques in a clean room environment, Balandin’s team built molybdenum disulfide transistors on silicon substrates for high-temperature experiments. Some had just a few-layer (1-3) and others had more, multiple-layers (15-18). The relatively thick films were more thermally stable and demonstrated a higher mobility at elevated temperatures, according to Balandin.
By conducting direct current measurement, a technique applying constant voltage or current through the device for a relatively long time, researchers studied the current-voltage characteristics or functional performance of the fabricated transistor at temperatures from 300 Kelvin to 500 Kelvin. They found that the device performed differently but remained functional as the temperature increased.
“Both mobility and threshold voltage decrease with temperature,” Balandin said. “Decreasing mobility results in current decrease through the device channel, while decreasing threshold voltage leads to current increase. Therefore, the exact behavior of current with increasing temperature would depend on the interplay of decreasing mobility and threshold voltage.”
Another intriguing feature researchers observed is a characteristic “kink” on the current-voltage graph at the zero voltage for temperatures higher than 450 Kelvin. This “memory effect” is similar to one observed in graphene transistors and electron glasses and suggests the material’s potential for use in high-temperature sensors.
According to Balandin, practical application of molybdenum disulfide transistors in control circuits or sensors at high temperatures requires operation longer than one month. As the team studied after two months, the aged devices demonstrated a stable operation, and were characterized by a higher threshold voltage, lower mobility and weaker temperature dependence of the mobility.
The researchers’ next step is to study the high-temperature function of molybdenum disulfide transistors and circuits, fabricated by industrial methods such as chemical vapor deposition.
###
For More Information:
Jason Socrates Bardi
+1 240-535-4954
jbardi@aip.org
@jasonbardi
Article Title
Authors
Chenglong Jiang, Sergey Roumyantsev, Rameez R. Samnakay, Michael S. Shur, and Alexander A. Balandin
Author Affiliations
University of California, Riverside and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
