Experiments in California demonstrate that collective movements of small zooplankton between water depths create large-scale current patterns with circulation effects as large as wind or tides
From the Journal: Physics of Fluids
WASHINGTON, D.C., September 30, 2014–Sea monkeys have captured the popular attention of both children and aquarium hobbyists because of their easily observable life cycle — sold as dehydrated eggs, these tiny brine shrimp readily hatch, develop and mate given little more than a tank of salt water.
Physicists, though, are interested in a shorter-term pattern: Like other zooplankton, brine shrimp vertically migrate in large groups in response to changing light conditions, coming closer to the surface at night and retreating deeper during the day.
Two researchers at the California Institute of Technology have shown experimentally that this pattern creates water currents much larger than the sum of those created by individual organisms in the group. Their results, published in the journal Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, suggest that the collective movement of small marine organisms could affect global ocean circulation patterns on a level comparable to the wind and the tides.
Because brine shrimp (Artemia salina) display phototaxis, a tendency to move towards a light source, researchers Monica Wilhelmus and John Dabiri used lasers to herd a swarm of the small crustaceans in a large water tank and induce a vertical migration pattern. A blue laser rising along the side of the tank caused the brine shrimp to move upwards; a green laser above the tank kept them centered. To visualize the resulting currents, they mixed microscopic silver-coated glass spheres into the water and captured their changing distribution throughout the migration with a high-speed camera.
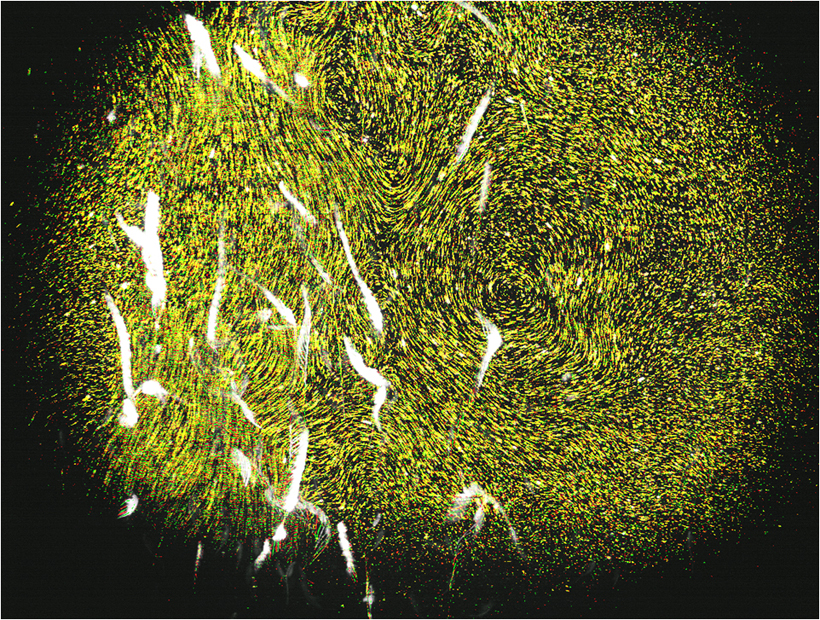
Previous studies have examined the tiny disturbances created when single plankton move through the water. Taken individually, these currents are not strong enough to impact broad ocean flow patterns. However, when two or more organisms swim in close proximity to each other as they did in this experiment, the eddies that they create interact to create more powerful swirling fluid forces that could alter water circulation on a wider scale.
“This research suggests a remarkable and previously unobserved two-way coupling between the biology and the physics of the ocean: the organisms in the ocean appear to have the capacity to influence their environment by their collective swimming,” said Dabiri.
Currents distribute salt, nutrients, and heat throughout the oceans and have been attributed to winds and tides, but these results suggest that living organisms could also play a role. The findings provide experimental support for a theoretical model proposed by Dabiri’s group in a 2009 Nature paper, which analyzed the effect of jellyfish on ocean mixing and proposed that such a model could also apply to smaller organisms. Because small organisms make up the bulk of oceanic biomass, the researchers estimate that their movement patterns could contribute a trillion watts of power to the ocean — on par with the wind and the tides.
The researchers hope to replicate the experiment in a tank where water density increases with depth, more closely mimicking ocean conditions. “If similar phenomena occur in the real ocean, it will mean that the biomass in the ocean can redistribute heat, salinity and nutrients,” said Dabiri.
###
For More Information:
Jason Socrates Bardi
American Institute of Physics
jbardi@aip.org
240-535-4954
@jasonbardi
Article Title
Observations of large-scale fluid transport by laser-guided plankton aggregations
Authors
Monica M. Wilhelmus and John O. Dabiri
Author Affiliations
California Institute of Technology
