The genes, involved in both diseases, could serve as targets for diagnosis and treatment.
From the Journal: APL Bioengineering
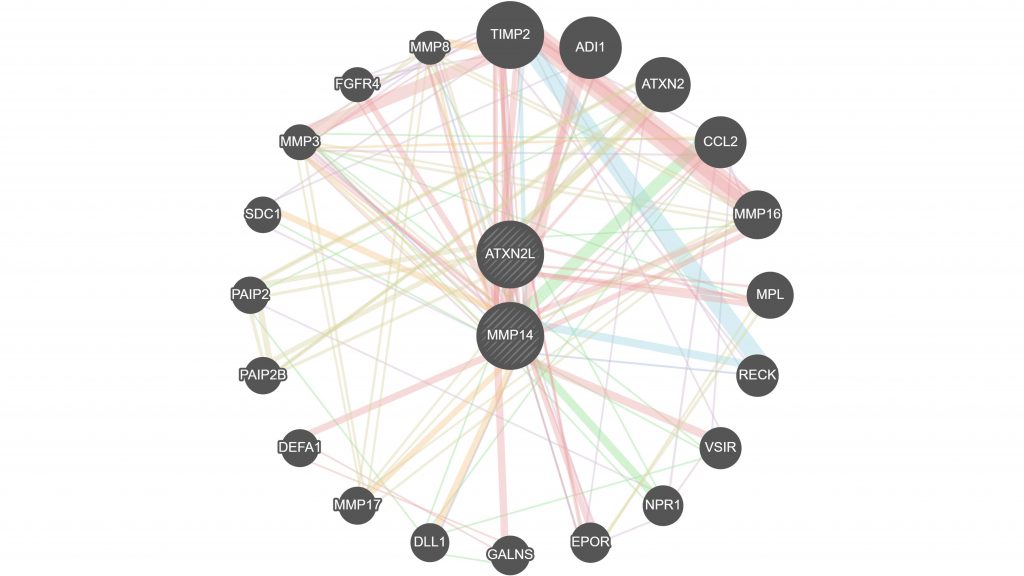
WASHINGTON, Nov. 5, 2024 – Rheumatoid arthritis is a common disease affecting an estimated 17 million people worldwide. The disease is caused by immune cells attacking the joints and can result in pain, swelling, and damage to the cartilage and bone. People with rheumatoid arthritis often develop osteoporosis, a more serious condition, as a result of the bone damage caused by immune cells and as a side effect of certain medications.
In APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing, researchers from Da-Chien General Hospital, China Medical University, and Chang Gung University employed analysis tools and machine learning algorithms to identify two genes linked to rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis that could serve as diagnostic tools and potential targets for treatments.
Both diseases center on one of the key mechanisms used to keep the rest of the body in check. Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a crucial tool immune cells use to remove malfunctioning or unneeded cells. However, malfunctions can lead to immune cells mistakenly targeting cells at random, with often disastrous results.
“In rheumatoid arthritis, excessive apoptosis of bone-forming cells contributes to joint destruction and inflammation,” said author Hao-Ju Lo. “This same process also leads to weakened bones in osteoporosis, emphasizing the need to manage both conditions simultaneously.”
Because of its central role, the researchers set out to find genes involved with apoptosis that were closely linked to both diseases. Drawing from a large database of genetic information, they gathered dozens of sequenced genomes from people with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis to look for any similarities. Combing through this mountain of genetic data was no easy task, so they turned to recently developed computational methods to narrow down their search.
“We used bioinformatics tools to analyze large gene datasets, focusing on genes active in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis,” said Lo. “We applied machine learning techniques, such as Lasso and Random Forest, to refine our search, identifying two key genes — ATXN2L and MMP14 — that play significant roles in both diseases.”
According to their analysis, these two genes are significantly associated with the progression of both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis. ATXN2L has a role in regulating processes like apoptosis, so malfunctions in this gene are likely to trigger both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis. MMP14 contributes to building extracellular tissue like cartilage and could be responsible for the breakdown of joint tissue that leads to rheumatoid arthritis.
“Our analysis revealed that these genes are involved in immune regulation and bone metabolism, suggesting they could be useful markers for diagnosing or treating both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis,” said Lo.
With two potential targets identified, the authors plan to use these results as a starting point to develop new treatment options for patients suffering from these two linked diseases.
“We plan to validate these findings with experimental studies and explore how targeting these genes could improve treatment outcomes,” said Lo. “Our future research may also involve developing personalized therapies, leveraging AI and machine learning to predict which patients are most at risk for osteoporosis.”
###
Article Title
Authors
Hao-Ju Lo, Chun-Hao Tsai, and Tsan-Wen Huang
Author Affiliations
Da-Chien General Hospital, China Medical University, Chang Gung University
