From the Journal: Physics of Fluids
WASHINGTON, December 15, 2020 — Even though it has been widely known that wearing a face mask will help mitigate the community spread of COVID-19, less is known regarding the specific effectiveness of masks in reducing the viral load in the respiratory tracts of those wearing them.
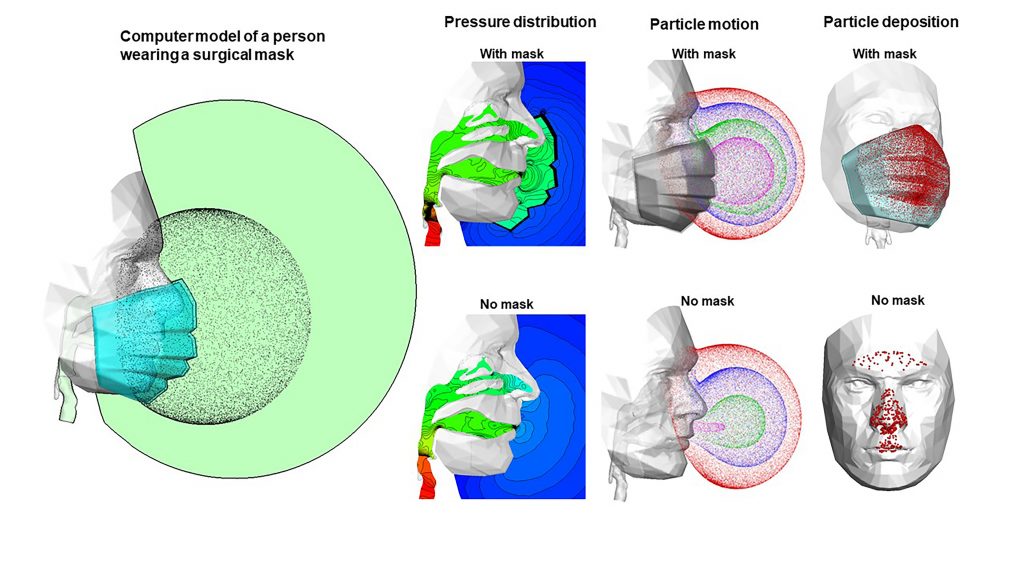
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Massachusetts Lowell and California Baptist University examined the effect of wearing a three-layer surgical mask on inspiratory airflows and the mask’s effects on the inhalation and deposition of ambient particles in the upper respiratory airways.
“It is natural to think that wearing a mask, no matter new or old, should always be better than nothing. Our results show that this belief is only true for particles larger than 5 micrometers, but not for fine particles smaller than 2.5 micrometers,” said author Jinxiang Xi.
The researchers found that wearing a mask with low (less than 30%) filtration efficiency can be worse than without.
They developed a computational face mask model using a physiologically realistic model of a person wearing a surgical mask with pleats and then using numerical methods to track the particles through the mask. They examined the behavior and fates of aerosols passing through the mask, onto the face, into the airway, and, eventually, where they deposit in the nose, pharynx, or deep lung.
The model showed a mask changes the airflow around the face, so that instead of air entering the mouth and nose through specific paths, air enters the mouth and nose through the entire mask surface but at lower speeds.
The lower speed near the face favors the inhalation of aerosols into the nose, so even though masks filter out certain numbers of particles, more particles escaping mask filtration can enter the respiratory tract.
They found the filtration efficiency of the three-layer surgical mask can vary from 65%, if new, to 25%, when used, so wearing a 65% mask properly will provide good protection, but wearing a 25% filtration mask can be worse than not wearing one at all.
“We hope public health authorities strengthen the current preventative measures to curb COVID-19 transmission, like choosing a more effective mask, wearing it properly for the highest protection, and avoid using an excessively used or expired surgical mask,” said Xi.
The researchers found the pleats of a surgical face mask significantly affect airflow patterns, suggesting that mask shape should also be considered as an important factor when estimating mask protection efficiency and designing new masks. Xi said they will further study the effects of mask shapes on human airway protection efficiency.
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
Authors
Jinxiang Xi, Xihua April Si, and Ramaswamy Nagarajan
Author Affiliations
University of Massachusetts Lowell and California Baptist University
