From the Journal: Chaos
WASHINGTON, D.C., September 24, 2019 — By studying the brain dynamics of 28 subjects with epilepsy, scientists demonstrated there is no evidence for a previously suspected warning sign for seizures known as “critical slowing down.”
In 2013, some of the first seizure-prediction devices were developed and successfully tested. Although extensive research efforts have successfully identified predictors of imminent seizures, the concept of critical slowing down as an index for seizure susceptibility has been controversial and remained unproven.
Critical slowing down refers to characteristic changes in the behavior of a complex system that approaches a theoretical tipping point. When this point is exceeded, it can lead to impactful and devastating changes. An epileptic human brain is considered an excellent example of a system such as this, due to the extreme and distressing nature of a seizure.
In a paper published in Chaos, from AIP Publishing, researchers investigated recordings of brain dynamics that captured 105 epileptic seizures using time-resolved estimates of early warning indicators of the seizures.
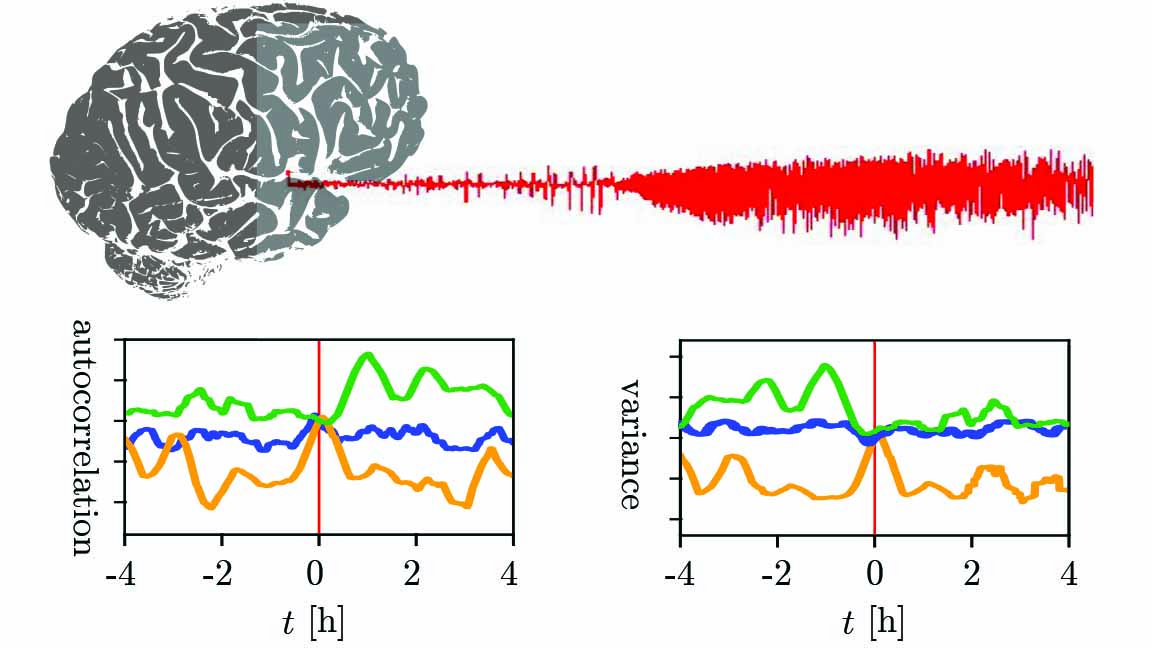
“In our investigations, we used the most prominent indicators and showed that critical slowing down prior to human epileptic seizures is not verifiable,” neurophysicist Thorsten Rings said. “This demonstrates that the concept underlying critical slowing down is too simple of a model for the human brain.”
Instead of critically slowing down, the researchers discovered the seizures acted oppositely and critically sped up, indicating the brain dynamics were less sensitive to changes and experienced a faster return to an unperturbed state.
“Similar indicators of critical slowing down can even be observed in relation to daily rhythms, such as sleeping and waking, but we lack clear-cut evidence for critical slowing down preceding such changes,” researcher Theresa Wilkat said. “Therefore, it is hard to clearly distinguish between a critical transition into a seizure and a critical transition into other states.”
An in-depth model of the transition into a seizure is still missing, but considering their research, Klaus Lehnertz and his team said the concept of critical slowing down is insufficient as a predictive method. They believe future studies should develop improved models and analysis techniques.
“A promising future approach might be to investigate how seizures emerge from large-scale brain networks by taking into account their time-varying structure and function,” Lehnertz said.
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
No evidence for critical slowing down prior to human epileptic seizures
Authors
Theresa Wilkat, Thorsten Rings and Klaus Lehnertz
Author Affiliations
University of Bonn
