From the Journal: Biomicrofluidics
WASHINGTON, June 9, 2020 — Our ability to predict who will get cancer, how a patient will respond to treatment, or if a patient will relapse is still quite limited. Despite advances in the detection of genetic mutations and the establishment of risk factors, such as age and genetic variants, it remains a great scientific and medical challenge.
University of California, Berkeley researchers Lydia Sohn and Molly Kozminsky were inspired to come up with new ways of looking at the problem. In the journal Biomicrofluidics, from AIP Publishing, they report that using cellular mechanophenotyping, along with traditional methods such as immunostaining and genetic analysis, may provide a more comprehensive view of a tumor.
“Our lab is interested in exploring markers that have biological implications in a cancer’s ability to develop and spread, and we wanted to highlight research that has been conducted to further the determination of mechanical properties of cells within preclinical settings,” said Sohn.
Cells naturally experience different forces within the body and, when cancer occurs, these forces can change, causing cells to no longer respond in their usual way to these forces. When cancer spreads, it encounters many hurdles put forth by the architecture of our bodies as well as by the immune system.
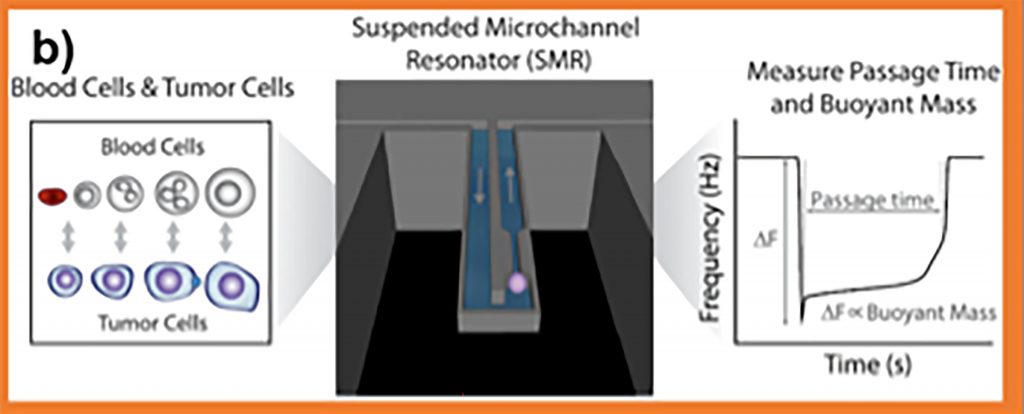
A cancer cell changes in many ways to complete a multistep process known as metastasis — traveling to other parts of the body — so the researchers focused on cellular mechanophenotyping, the field of research that investigates the mechanical changes a cell undergoes.
“Physical properties, like stiffness and viscosity, can be measured to see how a cell is changing and how these changes correspond with the disease state,” Kozminsky said.
The introduction of mechanical properties represents a major shift away from current diagnostic and monitoring paradigms.
“We are excited to share both the biological background behind these studies as well as technologies that have advanced to the point of being used to analyze clinical specimens,” said Sohn.
While reviewing the literature, the researchers saw new technologies but were surprised to find that only a small subset of them are being applied directly to patient samples.
“In general, we believe that even though some technologies, like atomic force microscopy, have been around for a long time, there’s still a great deal of room for growth of mechanophenotyping technologies,” Kozminsky said.
The researchers hope their work will inspire additional investigation into the mechanical properties of cancer cells, particularly as they pertain to clinical samples and disease progression.
“We also hope our work will motivate those developing new technologies to consider the necessity of benchmarking their systems with patient-derived samples,” said Sohn. “Mechanophenotyping of cells is still a nascent area of research, and it will be exciting to see it mature and the many contributions it will make clinically.”
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
The promise of single-cell mechanophenotyping for clinical applications
Authors
Lydia Sohn and Molly Kozminsky
Author Affiliations
University of California, Berkeley
