Tiny bubbles may have complex breaking mechanisms dependent on their surrounding solution
From the Journal: Applied Physics Letters
 WASHINGTON, D.C., September 28, 2017 — Nanobubbles have recently gained popularity for their unique properties and expansive applications. Their large surface area and high stability in saturated liquids make nanobubbles ideal candidates for food science, medicine and environmental advancements. Nanobubbles also have long lifetimes of hours or days, and greater applicability than traditional macrobubbles, which typically only last for seconds.
WASHINGTON, D.C., September 28, 2017 — Nanobubbles have recently gained popularity for their unique properties and expansive applications. Their large surface area and high stability in saturated liquids make nanobubbles ideal candidates for food science, medicine and environmental advancements. Nanobubbles also have long lifetimes of hours or days, and greater applicability than traditional macrobubbles, which typically only last for seconds.
The stability of nanobubbles is well understood, but the mechanisms causing their eventual destabilization are still in question. Using molecular dynamics simulations (MDS), researchers from the Beijing University of Chemical Technology explored the effect of surfactants — components that lower surface tension — on the stabilization of nanobubbles. They report their findings on the surprising mechanisms of destabilization for both soluble and insoluble surfactants this week in Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
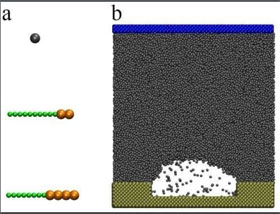
Researchers investigated the differences between soluble and insoluble surfactants and their varying influence on nanobubble stability using MDS software. They created a controled model system where the only variables that could be manipulated were the number of surfactants and the interaction between the surfactant and the substrate, the base of the model where the bubble is formed, to measure the direct influence of surfactants on nanobubble stability.
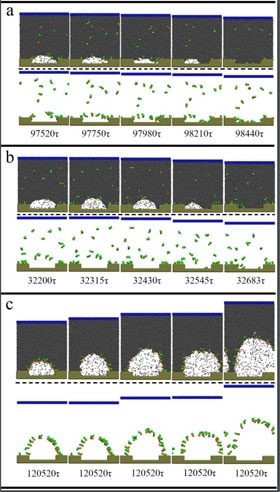
Analyzing both soluble and insoluble surfactants, the group focused on two possible mechanisms of destabilization: contact line depinning, where the surfactant flexibility reduces the forces responsible for stabilizing the bubble shape, causing it to rupture from lack of inner surface force; and surface tension reduction, causing a liquid to vapor phase transition.
The found soluble surfactants initiated nanobubble depinning when a large amount, roughly 80 percent, of the surfactant was adsorbed by the substrate, eventually causing the nanobubbles to burst.
“However, when small concentrations of soluble surfactant were introduced it remained dissolved, and adsorption onto the substrate was insignificant, generating a negligible effect on nanobubble stability,” said Xianren Zhang at Beijing University of Chemical Technology.
Simulations with insoluble surfactants showed comparable results to soluble surfactants when interacting heavily with substrates, but a new mechanism was discovered demonstrating a liquid-to-vapor transition model of bubble rupture.
The transition is similar to how we traditionally envision bubbles popping, occurring when a surfactant significantly reduces the surface tension on the outside of the nanobubble. Nanobubbles destabilize in this fashion when a large amount of surfactant is present, but little — around 40 percent — surfactant-substrate interaction occurs.
These findings are critical to understanding nanobubble stability and have implications for nanobubble interaction with other molecules, including proteins and contaminants. Nanobubble applications could revolutionize aspects of modern medicine such as ultrasound techniques, expand functions in food science, and improve waste water treatment. But better characterizing basic properties like instability is essential to fully utilizing their potential in these applications.
###
For More Information:
Julia Majors
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
@AIPPhysicsNews
Article Title
How nanobubbles lose stability: Effects of surfactants
Authors
Qianxiang Xiao, Yawei Liu, Zhenjiang Guo, Zhiping Liu and Xianren Zhang
Author Affiliations
Beijing University of Chemical Technology
