From the Journal: Applied Physics Letters
WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 — A wide variety of portable and wearable electronics have become a large part of our daily lives, so a group of Stanford University researchers wondered if these could be powered by harvesting electricity from the waste heat that exists all around us.
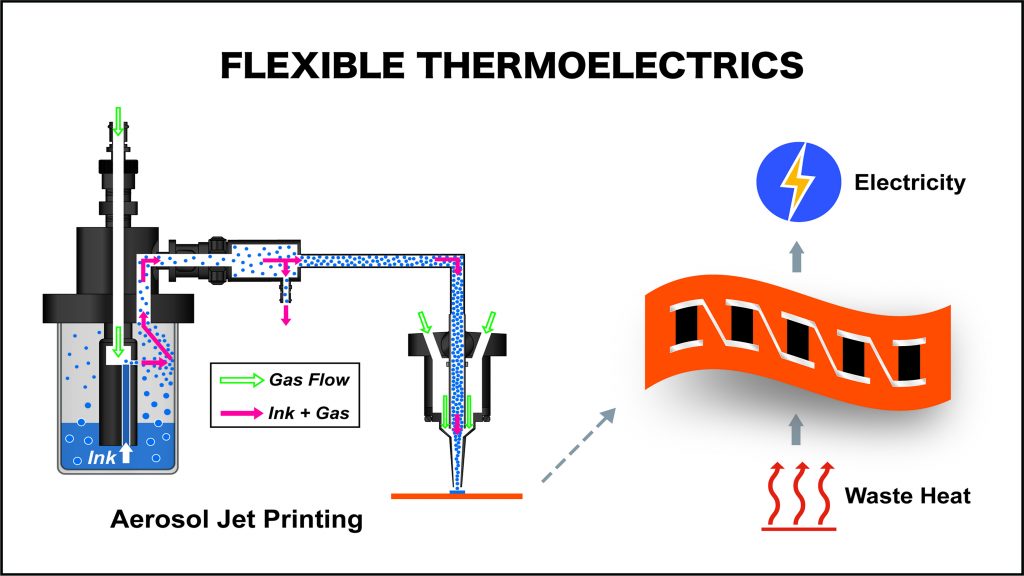
Further inspiration came from a desire to ultimately fabricate energy converting devices from the same materials as the active devices themselves, so they can blend in as an integral part of the total system. Today, many biomedical nanodevices’ power supplies come from several types of batteries that must be separated from the active portion of the systems, which is not ideal.
In Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, the researchers report the design and fabrication of single-wall carbon nanotube thermoelectric devices on flexible polyimide substrates as a basis for wearable energy converters.
“Carbon nanotubes are one-dimensional materials, known for good thermoelectric properties, which mean developing a voltage across them in a temperature gradient,” said Eric Pop, a professor of electrical engineering and materials science. “The challenge is that carbon nanotubes also have high thermal conductivity, meaning it’s difficult to maintain a thermal gradient across them, and they have been hard to assemble them into thermoelectric generators at low cost.”
The group uses printed carbon nanotube networks to tackle both challenges.
“For example, carbon nanotube spaghetti networks have much lower thermal conductivity than carbon nanotubes taken alone, due to the presence of junctions in the networks, which block heat flow,” Pop said. “Also, direct printing such carbon nanotube networks can significantly reduce their cost when they are scaled up.”
Thermoelectric devices generate electric power locally “by reusing waste heat from personal devices, appliances, vehicles, commercial and industrial processes, computer servers, time-varying solar illumination, and even the human body,” said Hye Ryoung Lee, lead author and a research scientist.
“To eliminate hindrances to large-scale application of thermoelectric materials — toxicity, materials scarcity, mechanical brittleness — carbon nanotubes offer an excellent alternative to other commonly used materials,” Lee said.
The group’s approach demonstrates a path to using carbon nanotubes with printable electrodes on flexible polymer substrates in a process anticipated to be economical for large-volume manufacturing. It is also “greener” than other processes, because water is used as the solvent and additional dopants are avoided.
Flexible and wearable energy harvesters can be embedded into fabrics or clothes or placed on unusual shapes and form factors.
“In contrast, traditional thermoelectrics that rely on bismuth telluride are brittle and stiff, with limited applications,” Pop said. “Carbon-based thermoelectrics are also more environmentally friendly than those based on rare or toxic materials like bismuth and tellurium.”
The most important concept in the group’s work is to “recycle energy as much as we can, converting uneven heat distribution to electrical energy for use for the next cycle of operation, which we demonstrated by using nontoxic nanotube-based thermoelectric generation,” said Yoshio Nishi, a professor of electrical engineering. “This concept is in full alliance with the world’s goal of reducing our total energy consumption.”
###
