From the Journal: APL Bioengineering
WASHINGTON, February 16, 2021 — The widespread use of high-speed and high-energy weapons in modern warfare has led to an increasing incidence of explosive injuries. For such wounds as well as those incurred in disasters and accidents, severe hemorrhage is the leading cause of death.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Southern University of Science and Technology in China examine the advances in hydrogel dressings in recent years, which are good at promoting wound healing and can better meet the demands of different situations.
“With the rapid developments of material science, there are numerous highly efficient wound dressings being developed,” said author Decheng Wu.
While bandages and gauzes are effective in controlling hemorrhage, they have various limitations. They are not biodegradable and are susceptible to infection and unsuitable for irregularly shaped wounds. They might also cause secondary tissue damage and are almost ineffective for wound healing.
Many hydrogel wound dressings are antibacterial, biodegradable, responsive, and injectable. Conventional dressings, in contrast, have a single function, making them less effective for wound treatment.
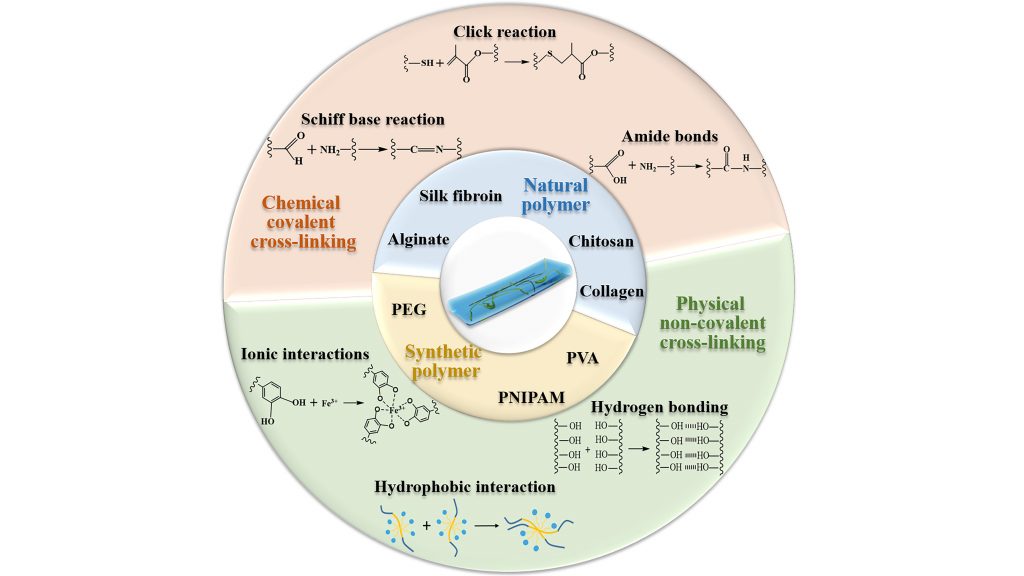
Hydrogel is a 3D network that is composed of hydrophilic polymers, which can absorb and swell in water. Hydrogels can be prepared by different cross-linking strategies, and they are classified in different ways based on their constitutes.
Polysaccharide-based hydrogels are biocompatible, biodegradable, and nontoxic. In contrast, synthetic polymer-based hydrogels are more easily modified and have better mechanical strength.
When used as a wound dressing, hydrogel not only forms a physical barrier and removes excess exudate but also provides a moisture environment that promotes the wound healing process. Additionally, hydrogel can perfectly fill irregularly shaped wounds and deal with deep bleeding efficiently.
The poor mechanical strength of existing hydrogel dressings limits their applications in the treatment of massive bleeding, such as arterial ruptures, since they cannot provide effective protection for the wound to prevent secondary damage. Consequently, the researchers will focus future research on developing hydrogel dressings with high mechanical strength so these dressings could help with fatal severe hemorrhage.
“Hydrogels are a kind of superior material,” said Wu. “In my opinion, high-performance hydrogels also have potential in the field of tissue engineering to replace some tissues that can self-heal and regenerate, such as annulus fibrosus, meniscus, and cornea.”
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
Recent advances on polymeric hydrogels as wound dressings
Authors
Zheng Pan, Huijun Ye, and Decheng Wu
Author Affiliations
Southern University of Science and Technology
