Technique can suppress infections and encourage healing around prosthetics without the problems caused by antibiotics and tissue grafting.
From the Journal: APL Bioengineering
WASHINGTON, Jan. 10, 2023 – Total hip and knee replacements are challenging enough for patients. When an infection occurs in the aftermath, the results are often disastrous, requiring potent antibiotics and revisionary surgery.
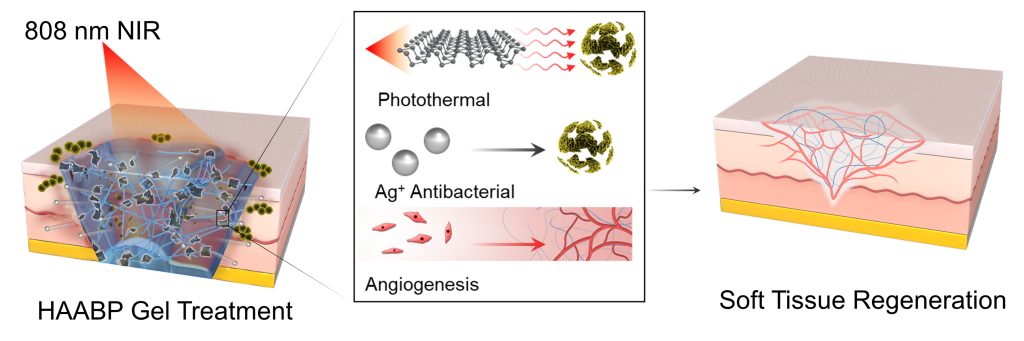
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine developed an injectable hydrogel that treats infections around prosthetics without the problems caused by current treatments. Testing showed that the gel inhibits common bacteria and promotes tissue regrowth.
After hip and knee replacement surgeries, pathogenic bacteria can adhere to the surface of the joint prosthesis and form a dangerous biofilm. Gold standard clinical methods use potent antibiotics and further surgery, including removal of infected tissue and transplantation of new tissue, to treat these infections. However, these strategies run into problems with hyper-resistant bacteria caused by the abuse of antibiotics, persistent damage caused by tissue removal, difficulties in obtaining tissue donors, and toxicity and immune system complications.
“It is important to explore a new strategy for treatment of infected soft tissue wounds because it is directly related to prognosis,” said author Ruixin Lin. “We aspire to develop a simpler, safer method to help more patients avoid suffering and help more doctors make the right choices.”
The team created the black phosphorus-enhanced antibacterial injectable hydrogel to reestablish biological barriers in soft tissue and suppress persistent infections. The gel has a porous structure, excellent injectability, and rapid self-healing properties.
In vitro tests showed the hydrogel had good stability and low toxicity to tissue cells. Irradiating the gel with near infrared light causes it to release silver ions. This process was highly efficient at inhibiting S. aureus, common bacteria that cause disease in humans.
“Furthermore, an in vivo infected wound model showed that the hydrogel could not only inhibit the persistent infection of the wound, but also accelerate the deposition of collagen fibers and angiogenesis, thereby realizing the repair of the natural barrier of soft tissue,” said Lin.
The novel hydrogel provides a safe and feasible synergistic antibacterial strategy for infected soft tissue healing. The team believes that it solves current clinical problems, such as stubborn infections caused by antibiotic resistance, and provides new ideas for minimally invasive treatment. They hope to see it used in the clinic after conducting sufficient studies on its underlying mechanisms.
###
Article Title
Black phosphorus-enhanced injectable hydrogel for infected soft tissue healing
Authors
Yaochao Zhao, Zhijie Chen, Wenjun Shao, Shu Yang, Wenguo Cui, Zhengwei Cai, Liang Cheng, and Ruixin Lin
Author Affiliations
Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
