A complex system economic model reveals how redistribution of wealth could prevent the spread of intolerance in the face of inequality.
From the Journal: Chaos
WASHINGTON, March 14, 2023 – In a world experiencing growing inequality and intolerance, tools borrowed from science and mathematics could be the key to understanding and preventing prejudice.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, Luis A. Martinez-Vaquero of the Polytechnic University of Madrid applied evolutionary game theory, which combines techniques from economics and biology, and complex system analysis to investigate the relationship between inequality and intolerance. He found that inequality boosts intolerance and that redistribution of wealth can prevent its infectious spread.
Martinez-Vaquero studied cooperation using an indirect reciprocity model. Unlike direct reciprocity, where individuals base their decisions only on the past encounters with the specific individuals they are interacting with, indirect reciprocity relies on a third party. In this case, individuals assign other individuals reputations based on the actions they witness. They base future encounters on that reputation.
“Thus, strategies under reputation-based indirect reciprocity consist of two parts: moral assessments, which dictate how individuals judge the interactions of others and attribute reputations, and action rules, which indicate how one should interact with others based on what these reputations are,” said Martinez-Vaquero.
In this model, a population is divided between a high-income group and low-income group. Individuals randomly interact in pairs as a donor or a recipient. The donor chooses if they want to contribute funds to the recipient based on both of their reputations.
The population witnesses the interaction and judges the donor’s action as “good” or “bad,” updating the donor’s reputation accordingly.
Tolerant individuals do not judge based on income when deciding to donate, while intolerant individuals will assign those from the opposite income group “bad” reputations. Intolerant individuals will also judge individuals from their group as “bad” for cooperating with the opposite group.
“Inequality clearly enhances the emergence of intolerance, escalating it even without the presence of new individuals who bring these behaviors. Once intolerance begins to act, it is almost unstoppable in the presence of inequality,” said Martinez-Vaquero.
In some scenarios, results also show that economically disfavored individuals from minority groups prioritized helping wealthy individuals over members of their group, even when wealthy individuals discriminated against them.
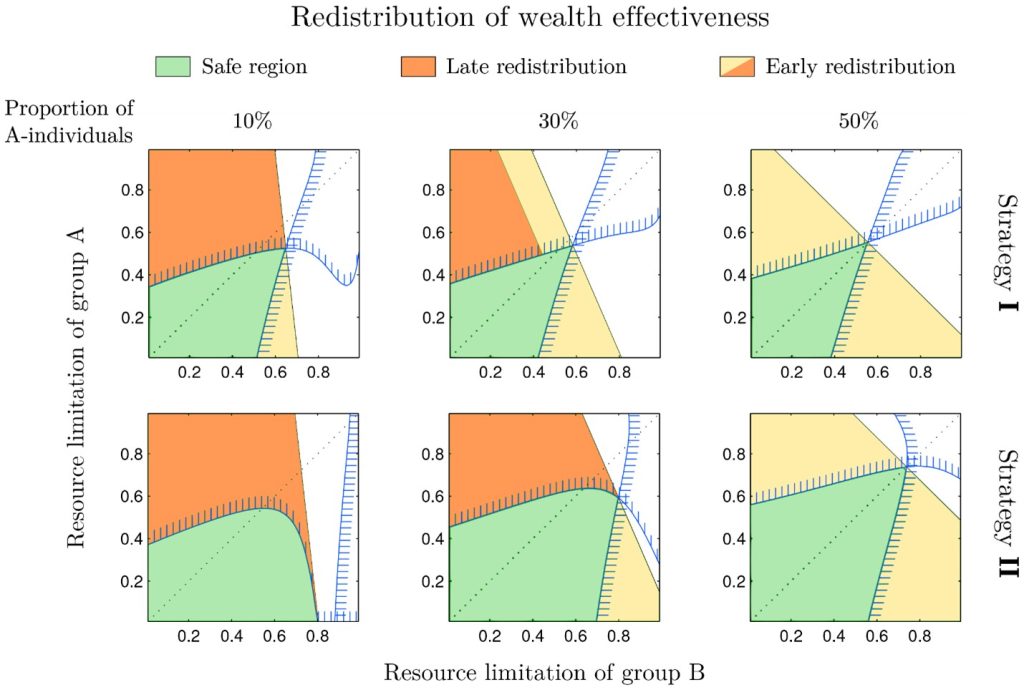
Still, redistribution of wealth early during the spread of intolerance proved an effective intervention.
This simplified model is a foundation for future investigation into preventing intolerance by intercepting wealth inequality. It demonstrates the power of complex systems, which are used across many fields including climate science, thermodynamics, chaos theory, and neural network computing.
###
Article Title
Inequality leads to the evolution of intolerance in reputation-based populations
Authors
Luis A. Martinez-Vaquero
Author Affiliations
Polytechnic University of Madrid
