Indian researchers have conducted analyses to electrically increase liquid flow in pump-free microfluidic devices
From the Journal: Physics of Fluids
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 10, 2016 – If you’ve ever eaten food while upside down – and who hasn’t indulged this chimpanzee daydream? – you can thank the successive wave-like motions of peristalsis for keeping the chewed bolus down and ferrying it into your stomach. In mechanical microdevices, this method of transport moves fluids without a separate pump– saving precious space in lab-on-a-chip and futuristic organ-on-a-chip devices – but this transport method is difficult to finely control.
To remedy this, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology’s Advanced Technology Development Center in Kharagpur, West Bengal have conducted lubrication theory-based analyses to explore the hydrodynamic effects of improving flow rate in pre-existing peristaltic hardware relying on an external electric field. Their research, which assesses the combined effects of electric fields and peristalsis on the channel flow rate, appears this week in Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing.
“Through our theoretical analysis, we’ve shown that by keeping the same peristalsis hardware, we may obtain an enhanced on-the-fly controllability of the flow rate by augmenting the device with electric fields,” said Suman Charkraborty, a professor in the institute’s Mechanical Engineering Department, and the Head of its School of Medical Science and Technology.
According to Chakraborty, an electric field component can easily be implemented because existing microtubule fabrication often involves sputtering electrodes onto the ends of the tubes – when a field is switched on, these electrodes cause fluid flow by attracting charged fluid toward the compatible electrode.
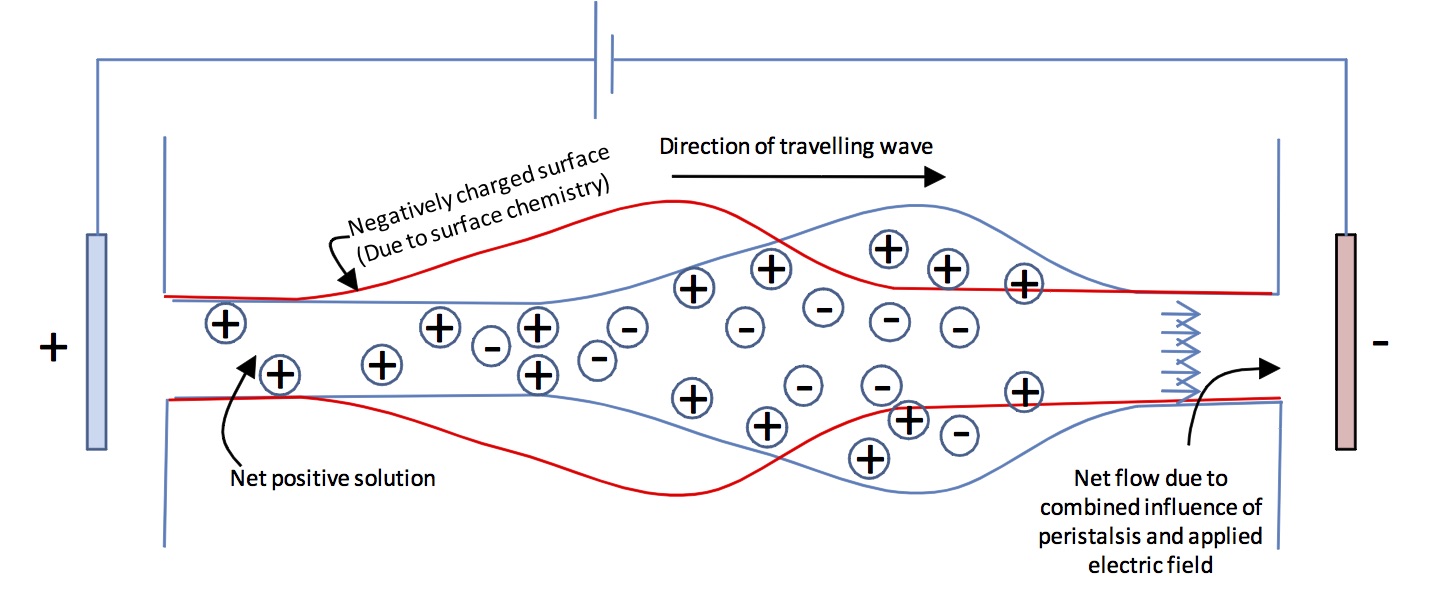
This has the potential to aid researchers in studying targeted drug delivery, augmenting biophysical fluid transport in human bodies, and observing and controlling chemical reaction and mixing in surface-modulated fluid flow environments, Chakraborty said.
Future work for Chakraborty and his colleagues includes analyzing the motion of charged particles in the electroosmotically-modulated peristaltic environment – a tricky matter, due to the interactions between fluidic drag, fluid flow via the electric field, and electrophoretic particle motion. The researchers are also working to develop nanoscale energy harvesting, microfluidics-based portable kits for rapid medical diagnostics, and microfluidic tools to deepen our understanding of the physiological dynamics of living systems.
###
For More Information:
AIP Media Line
301-209-3090
Article Title
Electroosmosis-modulated peristaltic transport in microfluidic channels
Authors
Aditya Bandopadhyay, Suman Chakraborty; Dharmendra Tripathi
Author Affiliations
Advanced Technology Development Center, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur, West Bengal, India; Department of Mechanical Engineering, Manipal University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
