From the Journal: Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy
WASHINGTON, August 18, 2020 — As the climate of the planet is changing, as evidenced by record-setting hot summers and extreme weather events, many researchers are looking to more renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind farms.
In a paper for the Journal of Sustainable and Renewable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers investigate whether the power generated by solar and wind farms would differ between current and future climates.
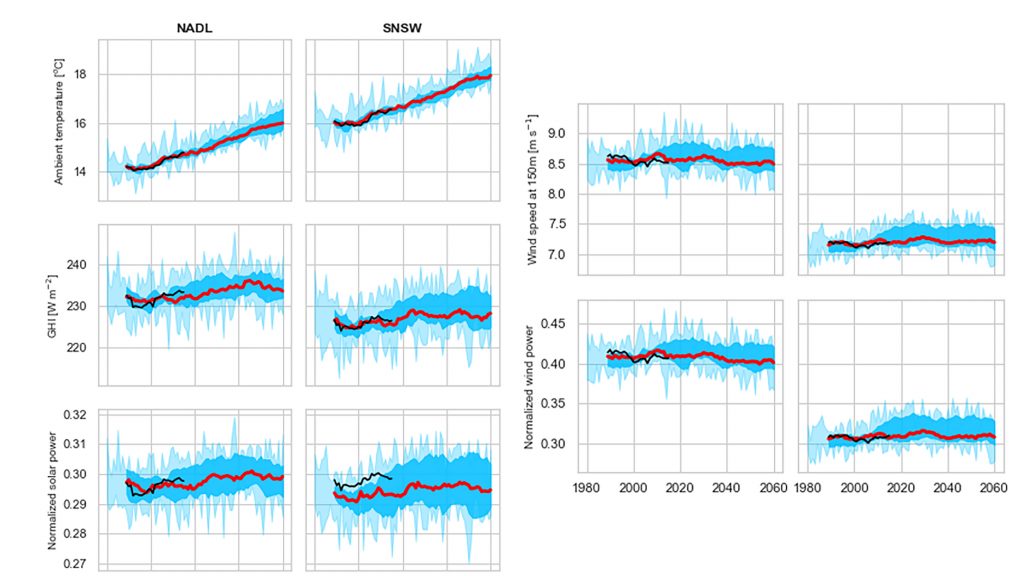
The researchers focused on Australia, since it is an ideal case study with extreme weather events, such as bush fires and windstorms. The sites selected were near Adelaide in South Australia and in southern New South Wales, where variable renewable generators are located or are likely to be located in the future based on the Australian Energy Market Operator’s system plan.
The researchers analyzed key weather variables, such as temperature, surface solar irradiance and wind speed, in 30-minute intervals for the years 1980 to 2060.
“We found that the general temporal trends in annual solar and wind power generation due to climate change are small, being at the order of 0.1% of its average production per decade,” said Jing Huang, one of the authors.
During the five hottest days of every year, however, the effect of climate change on renewable energy production was more severe. During these peak temperature days that coincided with peak energy demand and peak prices, solar power production was down 0.5%-1.1%, and wind farm production decreased between 1.6%-3% per decade.
The researchers’ findings are geared to inform the electricity sector about the reliability of interconnected power networks in different temperature conditions. Central power operators, for instance, need to plan for all contingencies to avoid power blackouts.
While this study looked at two sites in Australia, quantifying temperature impacts on renewable energy generation can be generalized to other areas beyond Australia.
“For different regions, there are different effects of climate change,” said Huang.
He said it will be important to conduct more case studies in other areas and climate regions to examine spatial climate variability and couple the findings with other aspects of energy systems, such as load and transmission infrastructure.
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
Authors
Jing Huang, Ben Jones, Marcus Thatcher and Judith Landsberg
Author Affiliations
Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation
