From the Journal: APL Materials
WASHINGTON, September 28, 2021 — Bioelectrical sensors on the skin can be used to measure electrical signals in the body, like heart activity and muscle contraction. While that provides valuable information for clinicians, current bioelectrical sensor technology can be ineffective, uncomfortable, expensive, and difficult to manufacture.
In APL Materials, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Utah and Gyeongsang National University in South Korea have developed a bioelectrical sensor that is convenient and low-cost.
The sensor measures electromyography (EMG) signals that are generated in muscles when they contract. EMG signals are useful for studying muscle fatigue and recovery, and they have the potential to inform diagnosis and treatment of neuromuscular diseases.
“The signal we measure is a voltage over a time,” said author Huanan Zhang. “Every time your finger moves, the potential of the body, of the muscle, changes. So, we are able to detect that difference in potential.”
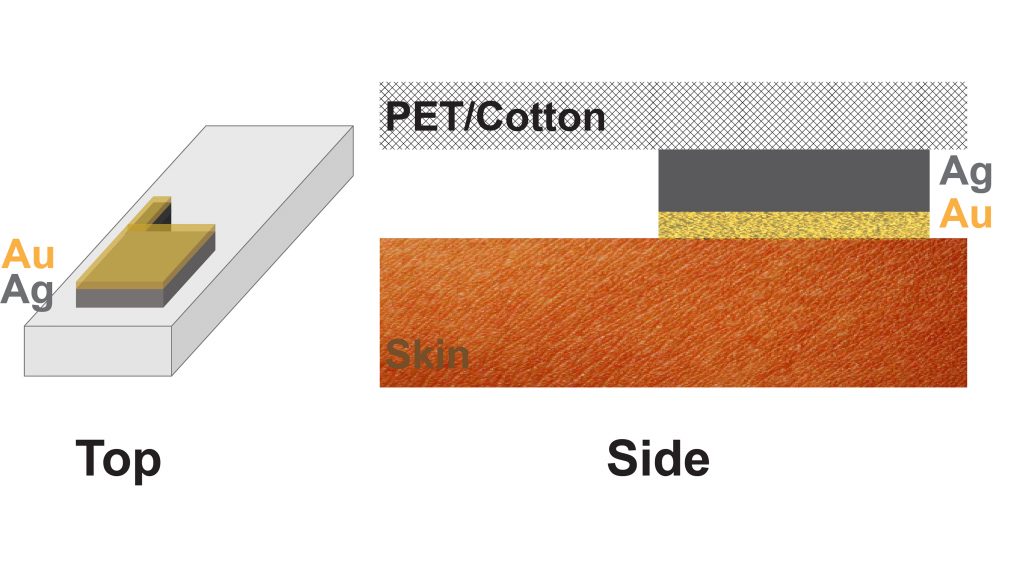
The biosensor is directly integrated onto a piece of clothing. That has advantages beyond convenience and comfort– soft clothing means better contact with the skin and a better signal.
Initially, the researchers printed silver paste directly onto fabric. Silver is conductive, making it a good material for detecting electrical signals. However, it is also somewhat toxic, so prolonged exposure can lead to skin irritation.
To harness the beneficial properties of silver while solving the problems it poses, the team deposited a layer of gold nanoparticles on top of the silver. The gold completely encapsulated the silver particles, preventing them from touching the skin.
The result was a detector that was both conductive and nonirritating to the skin. The amounts of gold and silver are small enough that it remains inexpensive as well.
The scientists tested the biosensor’s performance by placing it on the bicep and fingers and monitoring the detected signal as those muscles progressed through various exercises.
Because the sensor is part of the fabric and is designed to be used over long periods of time, it needs to withstand washing. The team retested sensor performance after multiple washings and found its performance remained high.
“This work not only designs a wearable device, which has the convenience factor, but it also has great performance and is biocompatible,” said Zhang.
The team believes that using this printing technique on textiles could revolutionize future bioelectrical sensors.
###
For more information:
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
301-209-3090
Article Title
Authors
Sohee Lee, Taehwan Lim, Huanan Zhang
Author Affiliations
University of Utah, Gyeongsang National University
