Sizing techniques play an essential role in the design of renewable energies for hybrid energy systems, and now, a team of researchers is using a "fuzzy logic" algorithm to determine optimal sizing for hybrid photovoltaic panel/battery systems
From the Journal: Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy
WASHINGTON, D.C., February 24, 2015 — How did fuzzy logic help a group of researchers in Tunisia and Algeria create an ideal photovoltaic system that obeys the supply-and-demand principle and its delicate balance?
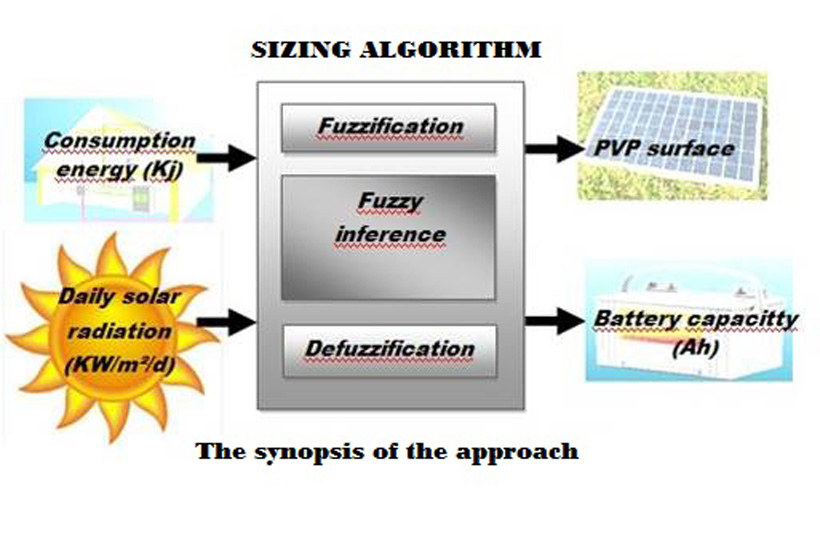
In the Journal of Renewable & Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, the group describes a new sizing system of a solar array and a battery in a standalone photovoltaic system that is based on fuzzy logic — a many-valued logic system designed to reason outputs by considering a range of possibilities rather than a simple, binary yes or no, as with classical logic.
“The fuzzy logic system accepts the consumed energy and the monthly average of daily solar radiations as inputs and then outputs photovoltaic panel surfaces and the battery capacity,” explained Chokri Ben Salah, a researcher in the Control and Energy Management Lab in the Department of Electrical Engineering at the National School of Engineers of Sfax, as well as an assistant professor at the Higher Institute of Applied Science and Technology of Sousse in Tunisia.
“Our method applies Matlab/Simulink interfaces, which aren’t complicated compared with other forms of simulation and model-based design,” said Ben Salah. In fact, it’s possible to build up a graphic integrated user interface to facilitate the usage of the proposed system. The group verified system performance with different inputs by simulations using calculated outputs.
Their results demonstrated the effectiveness of this approach, Ben Salah added. For example, an expansion-planning model of photovoltaic panels and battery systems for a domestic “smart” house performed well in simulations.
The sizing photovoltaic/battery system provides the capacity of batteries used in the hybrid system and determines the surface of the PVP to be used. Its primary significance is “characterized by its simplicity in the usage and its efficiency in optimizing the cost and losses,” they report.
In terms of applications, the system may find use in a number of areas, including domestic dwellings, public buildings and industrial electrical settings, as well as for agricultural water pumping in the field.
What’s the next step for the team’s work? “An extension of the present system is possible — such as appending a wind or fuel cell energy source,” noted Ben Salah. “Our system can also be improved by adding an electrolyzer system to permit it to convert lost photovoltaic solar energy into hydrogen that can be stored in a special tank and then be used elsewhere.”
###
For More Information:
Jason Socrates Bardi
+1 240-535-4954
jbardi@aip.org
@jasonbardi
Article Title
New optimally technical sizing procedure of domestic photovoltaic panel/battery system
Authors
Chokri Ben Salah, Kheireddine Lamamra and Anis Fatnassi
Author Affiliations
National School of Engineers of Sfax (Tunisia), University of Bejaia (Algeria), National School of Engineers of Monastir (Tunisia)
