Sea ice coverage is difficult to predict short-term, but sea ice health is crucial for the global climate.
From the Journal: Chaos
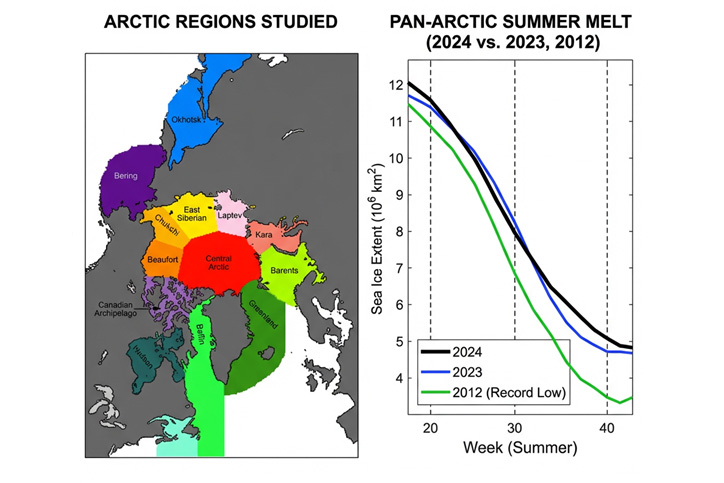
WASHINGTON, Feb. 3, 2026 — Arctic sea ice has large effects on the global climate. By cooling the planet, Arctic ice impacts ocean circulation, atmospheric patterns, and extreme weather conditions, even outside the Arctic region. However, climate change has led to its rapid decline, and being able to make real-time predictions of sea ice extent (SIE) — the area of water with a minimum concentration of sea ice — has become crucial for monitoring sea ice health.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the United States and the United Kingdom reported accurate, real-time predictions of SIE in Arctic regions. Sea ice coverage is at its minimum in September, making the month a critical indicator of sea ice health and the primary target of the work.
“Indigenous Arctic communities depend on the hunting of species like polar bears, seals, and walruses, for which sea ice provides essential habitat,” said author Dimitri Kondrashov. “There are other economic activities, such as gas and oil drilling, fishing, and tourism, where advance knowledge of accurate ice conditions reduces risks and costs.”
The researchers’ approach treats sea ice evolution as a set of atmospheric and oceanic factors that oscillate at different rates — for example, climate memory at long timescales, annual seasonal cycles, and quickly changing weather — while still interacting with one another. They used the National Snow and Ice Data Center’s average daily SIE measurements from 1978 onward to find the relationships between these factors that affect sea ice.
Testing their prediction method live in September 2024, and retroactively for Septembers of past years, the group confirmed their technique is generally accurate and can capture effects from subseasonal to seasonal timescales. They predicted SIE ranging from one to four months out and found their predictions outperformed other models.
In general, long-term climate forecasts tend to be easier and more reliable than short-term predictions. However, by incorporating regional data into their model, the researchers were able to improve short-term ice and weather estimates.
“The model includes several large Arctic regions composing [the] pan-Arctic,” said Kondrashov. “Despite large differences in sea ice conditions from year to year in different regions, the model can pick it up reasonably accurately.”
The group plans to improve their model by including additional oceanic and atmospheric variables, such as air temperature and sea level pressure. These variables can cause fast changes and short-term fluctuations that are not currently reflected in the model, and the researchers hope these additions will further enhance the predictability of summertime Arctic sea ice.
###
Article Title
Accurate and robust real-time prediction of September Arctic sea ice
Authors
Dimitri Kondrashov, Ivan Sudakow, Valerie N. Livina, QingPing Yang
Author Affiliations
University of California, Los Angeles; Open University; SETI Institute; National Physics Laboratory; Brunel University of London
